Sun protection can be a major challenge for athletes. Outdoor athletes have to train for long hours under the sun; hence, they cannot be consistent with the sun protective measures.
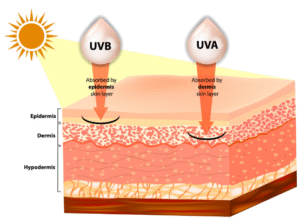
UV radiation is composed of UVC, UVB, and UVA. UVC radiation gets blocked by the atmosphere; UVA and UVB reach the surface of the earth and penetrate the skin. UVB is stronger than UVA and penetrates into the epidermis, while UVA penetrates the dermis layer of the skin. Sunscreen can prevent the UV radiation from absorbing into the skin.
You must be careful while choosing the sunscreen; you should consider factors like SPF and PA. SPF is determined by complex testing methods, which involve two methods—in vivo and in vitro SPF testing.
Understanding In Vivo and In Vitro SPF Testing methods
In Vivo Testing: This method is usually performed on animals or human beings and is considered the gold standard way for determining the SPF. SPF sunscreen is applied to the human volunteers, and they are then exposed to the UV light to determine the redness caused by the amount of UV radiation.
Cons: In vivo testing can be more challenging, expensive, and time-consuming; additionally, results vary, and there are some ethical concerns about exposing the volunteers to harmful UV radiation for in vivo tests.
Pros: Consumers have more trust in in vivo results because they are tested on humans.
In Vitro Testing: In vitro testing is usually done in a laboratory. A thick, even layer is applied to the plate made with polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). The SPF is then tested with the help of a spectrophotometer measuring device.
Cons: Because it is tested in a laboratory, the results might not replicate the skin behavior while testing.
Pros: Lower cost, suitable for early formulation, and it consumes less time.
What Are the Types of Sunscreen?
There are 3 types of sunscreens based on the active ingredients (UV filters) and their mechanisms of action.
Physical Sunscreen (Mineral): Physical sunblocks create a physical barrier on the skin by reflecting and scattering the UV rays away. Physical sunscreens usually contain zinc oxide and titanium dioxide; these active ingredients are the best broad spectrum and are effective in blocking UVA and UVB.
Pros:
- It works immediately and protects your skin.
- It is gentle on the skin and does not cause irritation or any stinging sensation around the eyes.
Cons:
- Physical sunscreen is usually thick, difficult to absorb into the skin, and can leave a white cast.
- It has a thick texture and can feel heavy on the skin.
Chemical Sunscreen: Often known as organic sunblock, they act as a sponge and absorb the UV rays that fall on the skin. They are believed to protect the tissue skin by absorbing the UV rays and converting them into heat or light, which is less dangerous. Chemical sunblocks contain active ingredients like avobenzone, oxybenzone, octinoxate, octisalate, octocrylene, and homosalate.
Note: There are other organic UV filters (European filters) like Tinosorb S, Tinosorb M, Mexoryl SX, and Mexoryl XL.
Pros:
- It is lightweight and easily gets absorbed into the skin.
- It does not leave a white cast and is often water resistant.
- It is suitable for the active lifestyle or to wear under makeup.
Cons:
- Chemical sunblock does not provide immediate protection; it needs 10-30 minutes for it to get activated after application.
- It might cause irritation around the eyes.
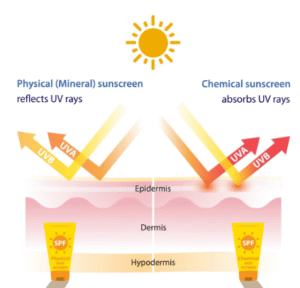
Hybrid Sunscreen: It contains the blend of physical and chemical UV filters.
Pros: It has a blend of chemical and physical filters that are gentle.
Cons: It can leave a slight white cast.
Sunscreen spray, lotion, or stick? Which to consider?
- Sunscreen Spray:
Pros: It is very convenient; you can apply it to a large area like back acne.
Cons: There is a risk of inhaling the spray.
- Sunscreen Stick:
Pros: It is very convenient for reapplying; it is portable and can be worn under makeup.
Cons: It does not apply evenly.
- Sunscreen Gel/Lotion/Cream:
Pros: Very reliable; you can use the right quantity, and it can be used daily.
Cons: Sunscreen creams can be heavy and can leave a white cast.
Best Sunscreen for Athletes—In Vivo and In Vitro SPF Tested
Here are a few of the best sunblocks for athletes, which are dermatologically tested and suitable for the Indian climate. All the following sunscreens have been tried and tested; here are my personal takes.
Physical Sunscreens
Some of the best physical sunscreens with amazing coverage and protection are:
1. Blue Lizard:
Reasons to Buy ✔: If you are extra-extra sensitive to sun rays like me, then this is the best sunscreen to use. It does not have any fragrance and does not cause any irritation around the eyes. It provides coverage for 1-2 hours and is water and sweat resistant.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It is thick in consistency and can take time to blend and activate.

2. EltaMD UV Clear Face Sunscreen
Reasons to Buy ✔: It’s a good sunblock, has a light texture, and blends easily. I could see a few dark spots fade away after regularly using it, since it consists of niacinamide, vitamin B3, and vitamin E. It provides sun protection for up to 1-2 hours.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It feels slightly irritating around the eyes and the nose area.

3. SunScoop Mineral SPF 50 PA++++
Reasons to Buy ✔: It is a good physical sunscreen suitable for combination, normal, and dry skin, but it is not that effective for sensitive skin. It is non-greasy, not heavy on the skin, and easily blendable.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It consists of a strong fruity fragrance, and it’s difficult to squeeze out the product from the tube. It may slightly leave a white cast.

4. Photon 360 Hydra
Reasons to Buy ✔: The sunscreen formulation is good; it is not oily or greasy on the skin. It provides good protection for up to 1-2 hours, and it is sweat- and water-resistant.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It takes time to blend into the skin.

Chemical Sunscreen:
Some of the best chemical sunscreens with amazing coverage and protection are:
1. ISNTREE Hyaluronic Acid Daily Sun Gel
Reasons to Buy ✔: This is the most underrated Korean sunscreen. It blends seamlessly and does not have any kind of fragrance. It keeps the skin moisturized, and you don’t need to use any additional moisturizer. It blends seamlessly and leaves no white cast. You will not feel any irritation around the eyes using this sunscreen. Even teen athletes can use this product for skincare.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: You need to reapply it every 20-30 minutes, and it is slightly on the expensive side.

2. Beauty of Joseon Relief Sun Rice + Probiotics
Reasons to Buy ✔: It is the best sunscreen for everyday use and does not leave a white cast. It blends seamlessly and has a very mild fragrance. Amazing for combination, oily, and normal skin. It does not make your skin greasy.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It is a slightly expensive sunscreen. It can cause a slight tingling sensation around the eyes. Also, it does not sit well under heavy makeup; it can make makeup look cakey.

3. Bioré Aqua Rich Watery Essence
Reasons to Buy ✔: It is one of the best Japanese sunscreens; it did wonders for my skin; it provides a cooling sensation and blends into your skin seamlessly without leaving any white cast. It keeps your skin very well moisturized and hydrated. You can use this sunscreen under makeup. You can add this product to your skincare regimen.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It has a strong alcohol smell; avoid this sunscreen if you have migraines—it can be difficult to bear the fragrance.

4. The Derma Co 1% Hyaluronic Sunscreen Aqua Gel
Reasons to Buy ✔: It is suitable for all skin types, as it is lightweight, non-greasy, and leaves no white cast. It has vitamin E and hyaluronic acid, which help to minimize fine lines.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It provides sun protection for only 30-50 minutes. Requiring reapplication every 30-60 minutes.

Hybrid Sunscreen:
Choosing hybrid sunscreen can be very effective, as it provides a combination of both physical and chemical sunscreens.
1. Dr. Sheth's Ceramide & Vitamin C Sunscreen
Reasons to Buy ✔: It provides skin barrier protection, evens out fine lines, and is well suited for sensitive skin. It includes chemical and physical filters, offering deeper sun protection. It’s packed with vitamin C, adding a skin glow without leaving the skin greasy.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It takes time to blend into the skin; you have to reapply the sunscreen every 45 minutes.

2. Dr. Sheth's Kesar & Kojic Acid Sunscreen
Reasons to Buy ✔: It contains the goodness of kojic acid and kesar, which has helped me in reducing micro pigmentation, tan, and acne scars. It is a paraben and sulfate-free formulation, safe for skin, dermatologically recommended, and suitable for Indian skin.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: It takes time to blend into the skin and can be cakey under the makeup; furthermore, the quantity of the product is very less.

3. Mamaearth Ultra-Light Indian Sunscreen
Reasons to Buy ✔: It is non-greasy and leaves no white cast. Overall, it’s a good product to try.
Reasons to Avoid 🧩: You will need to reapply the sunscreen every 30 minutes; it dries your skin and does not sit well under the makeup.

Which Sunscreen Types to Consider Based on Skin Types, Tones, and Texture?
Sunscreen recommendations by skin profiles: choosing the right sunscreen requires matching the formula to your specific skin needs.
1. Skin Types:
Oily/Acne Skin: Use chemical or hybrid, as they are lighter and less comedogenic.
Dry Skin: Physical or hybrid formulas are recommended. Physical sunscreens are generally less drying; consider physical sunscreen with hydrating ingredients like hyaluronic acid and glycerin.
Sensitive, Rosacea, and Eczema Skin: Physical sunscreens are the safest option due to their minimal absorption and irritation risk.
Normal Skin: Any sunscreens can be chosen based on preferences.
2. Skin Tone:
Fair to light skin tones: Consider using a physical sunscreen; since it leaves a slight white cast, it can act as a skin-brightening primer.
Medium to olive skin tones: Chemical or tinted chemical sunscreens are good options.
Deep/dark skin tones: Tinted chemical or any gel-formulated hybrid sunscreens are great options to avoid any visible white cast.
3. Skin Texture:
Rough/Uneven Texture/Large Pores: Chemical/tinted chemical or gel-based hybrid sunscreen will provide smooth application.
Mature Skin with Fine Lines: Use gel-based chemical sunscreen. Avoid any matte-finished sunscreens, which can highlight fine lines.
Skin with Hyperpigmentation/Melasma: Use physical sunscreen or tinted physical sunscreen, as they are physical blockers and provide more protection against harmful sunrays.
Types of Global and Indian Sunscreen Regulations and Restrictions
Indian Regulation:
- Sunscreen cosmetic regulation has replaced the older 2004 standard.
- SPF tested as per the COLIPA/ISO 24444:2019 protocols.
- Only 29 UV filters are accepted; many filters like Tinosorb S, Tinosorb M, Mexoryl XL, and Uvinul A Plus are not accepted in India.
USA (FDA):
- 16 filters are approved along with zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
- 12 chemical filters, including Avobenzone, Oxybenzone, Octinoxate, are under review
EU (European Union):
- More than 30 UV filters are approved
- Focus more on achieving balanced UVA protection.
Regulatory Trend 2025:
- US legislation, the SAFE Sunscreen Standards Act, is looking to modernize the FDA process and does not want to allow animal testing.
- It is looking to approve a few more European Tinosorb filters.
Final Thoughts:
Sunscreens are essential for not just athletes but for everyone. They provide protection from the harmful UVA and UVB rays. There are sunscreens with different formulations in the market. You will need to first understand your skin type, tone, and texture and what works best for your skin. This article covers everything, and all the products have been personally tried and tested. If you find the article helpful, then please share the article with friends and colleagues.
